Most people think that plagiarism is just stealing someone else’s work. However, there are different types of plagiarism other than directly copying others.
For example, did you know that you can even plagiarize yourself?
There are 8 different types of plagiarism that are pretty common:
- Complete Plagiarism
- Paraphrasing Plagiarism
- Self Plagiarism
- Direct Plagiarism
- Accidental Plagiarism
- Source Based Plagiarism
- Patchwork Plagiarism (Mosaic Plagiarism)
- AI Plagiarism
Plagiarism is a serious offense. It can lead to academic probation, failing your course, or irreversible damage to your reputation.
Knowing what these types of plagiarism are will help you avoid them easily. Let’s take an in-depth look at each.
ᴀᴅᴠᴇʀᴛɪsᴇᴍᴇɴᴛ
What Is Plagiarism
Plagiarism is taking the words and ideas of others and presenting it as yours. It is not only limited to research or academic writing. Copying creative property, like videos, images, music, art and even ideas is plagiarism.
We use the term ‘copying’ to be gentle. What it really amounts to is plain stealing. At its core it is unethical and strips you from the learning process.
There is no benefit to plagiarizing. The time you save is not worth the risks. The author you plagiarized from also does not get any credit. So it is unfair to them as well.
Common Types Of Plagiarism
| Type of Plagiarism | What It Is |
|---|---|
| Complete Plagiarism | Stealing the entirety of someone’s work |
| Paraphrasing Plagiarism | Only rewording other's words |
| Self Plagiarism | Using your previous essay or research and presenting it as new and original |
| Direct Plagiarism | Stealing significant portions from others |
| Source Based Plagiarism | Presenting your sources incorrectly or in a misleading way |
| Patchwork Plagiarism | Sprinkling copied material in yours without citation |
| Accidental Plagiarism | Unintentional plagiarism like forgetting to cite a source |
| AI Plagiarism | Getting AI to do the entire work for you |
8 Different Types Of Plagiarism Explained
Identifying plagiarism is easier when you understand the types there are. It helps you navigate through the subtle nuances of plagiarism and protects your reputation.
Here are the top 8 types of plagiarism you should to know as a student or a researcher:
1. Complete Plagiarism: Copying Someone’s Entire Work

This is a serious form of plagiarism where you directly take someone’s intellectual property and claim it as your own.
The severity of the offense comes from the fact that you intentionally stole it. Paying someone else to do the work for you and presenting it as if you did it is also another form of complete plagiarism.
Fortunately, you can easily avoid this. Simply do your own research and write the essay or paper yourself. An example of complete plagiarism would be you submitting an essay you found online. Complete plagiarism, or global plagiarism is pretty straightforward. However, others are a bit more nuanced.
2. Paraphrasing Plagiarism: Only Rewording Words Without Any Originality

Using other’s writing, or ideas but only changing a few things around without giving proper credit paraphrasing plagiarism.
Understanding paraphrasing vs plagiarism is key here. You may have presented it differently. Or used different words and sentence structures than the original author.
However, these by themselves aren’t enough. The idea is not yours. Plus, you did not credit the original author. That is the problem.
Many students unintentionally fall victim to paraphrasing plagiarism. An easy way to circumvent paraphrasing plagiarism is to give proper credit and cite your sources. Even a simple in-text citation is perfectly acceptable.
3. Self Plagiarism: Copying Your Previous Work

Yes, you can also plagiarize yourself. In simple terms, resubmitting your previous research or essay as new and original is self plagiarism.
If you're a student it could mean submitting the same essay you previously wrote for another course as new and original for the current course you are doing.
Although, if you use the same sources and cite properly, then you do not need to worry about plagiarism. Which means you can absolutely rely on your previous body of work. However, you cannot directly copy large amounts of it.
4. Direct Plagiarism: Stealing A Large Section Of Other’s Work

Copying a significant portion or a section from your reference material is direct plagiarism. This is slightly different from complete plagiarism. In complete plagiarism, you are copying the entirety of it.
So, direct plagiarism is closely related to complete plagiarism but there is a subtle difference.
What you should understand is that the issue of plagiarism only occurs when you’re not crediting the author. If you use proper quotations, maybe add in-text citations when needed, and also add full citations in your Bibliography, you will be fine.
ᴀᴅᴠᴇʀᴛɪsᴇᴍᴇɴᴛ
5. Accidental Plagiarism: Unintentionally Missing Citations Or Quotations

Accidental plagiarism can occur due to errors or forgetfulness. For example, you forgetting to cite a source, or not using quotes.
The previous four types of plagiarism could happen both intentionally and accidentally. Accidental plagiarism are always unintentional.
Even if you credit your sources but to it incorrectly, it would be accidental plagiarism. All these are accidental or unintentional plagiarism.
6. Source Based Plagiarism: Misleading Citations Or Bibliography

Source based plagiarism is an issue of misleading citation. For example, you took information from a secondary source.
But your source has taken that information from an original report or study. If you cite the original source, it is a form of source based plagiarism.
It is misleading because you have not actually looked at the original source yourself. This also tells you that plagiarism is not only limited to copying information or ideas. Understanding primary vs. secondary sources will help you avoid this type of plagiarism.
7. Patchwork Plagiarism (Mosaic Plagiarism): Piecing Together Words and Ideas

Sprinkling phrases, ideas or words of others without citation is patchwork plagiarism. It is also called mosaic plagiarism.
Patchwork plagiarism can be tricky to spot since it is so subtle. Especially if you are not using a good plagiarism checker.
This type of plagiarism can happen both accidentally and intentionally. A common example of this type of plagiarism would be copying a small phrase from your source and using it verbatim without any citation or quotation marks.
8. AI Plagiarism: Using AI To Do The Work For You

AI can plagiarize too. Getting an AI chatbot like ChatGPT to write your school essay for you is AI plagiarism. You did not write the essay yourself. You did not present your original idea, nor did you do any research. That is the problem. It is unfair to other students in your course too.
Although, in 2024, it is hard to ignore AI. You can certainly use AI for research. AI chatbots are also fantastic for generating ideas.
But using AI to generate the entire assignments or research papers is not recommended.
ᴀᴅᴠᴇʀᴛɪsᴇᴍᴇɴᴛ
What Percentage Of Plagiarism Is Acceptable?
The simple answer is that no percentage of plagiarism is acceptable. Your work should always be original. But a small percentage of plagiarism flagged by a tool is acceptable.
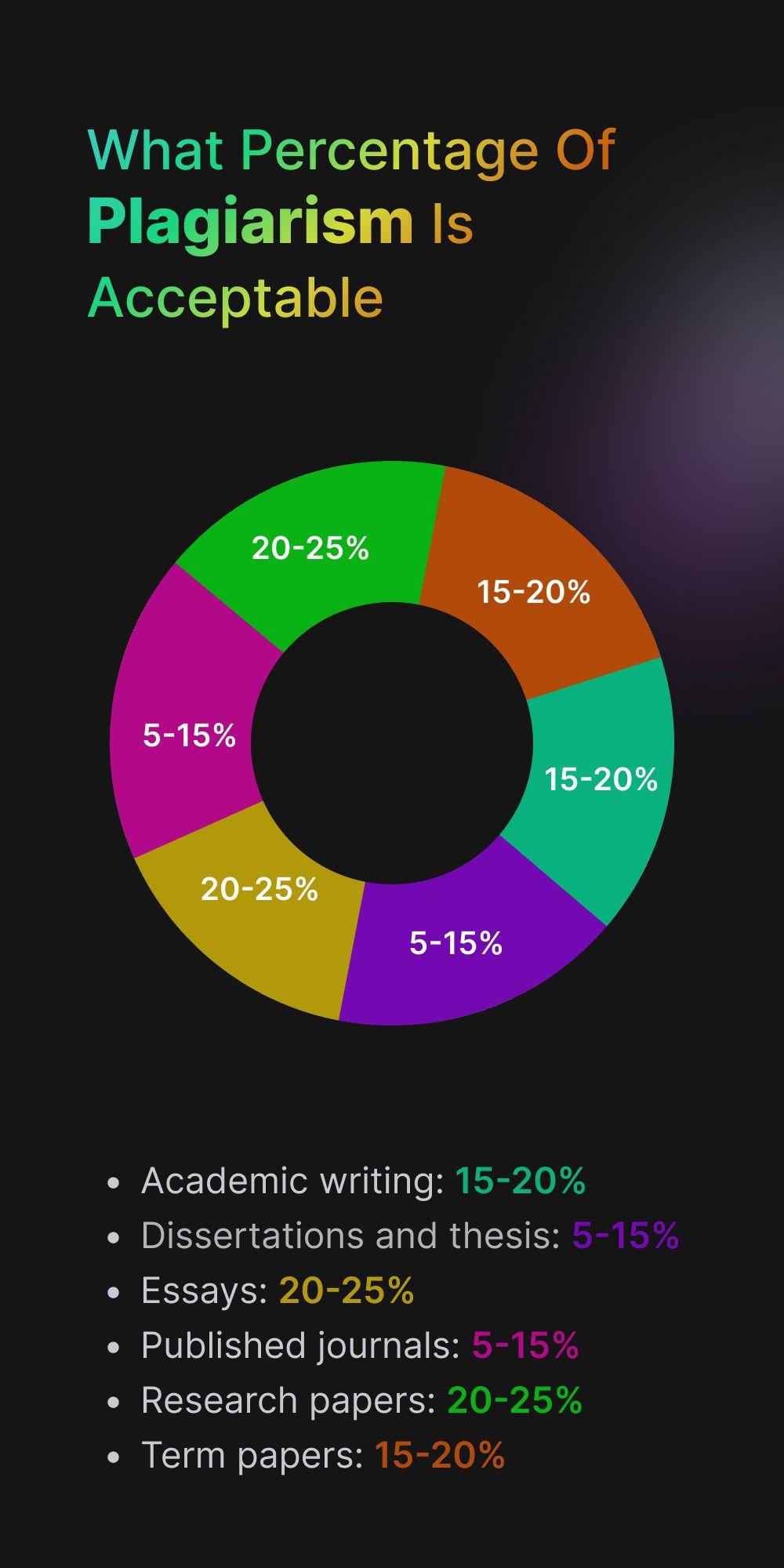
Some academic institutions typically allow 10 to 15% plagiarism. You have some leeway for research papers and published journals too. Different sources mention 5 to 15% as the acceptable limit for published journals.
Plagiarism checkers match phrases and look for similarities. That is why you will see some of these software flag a certain percentage of your document as plagiarism.
It is tricky because there is no agreed-upon standard for this. So, whether you’re a student, or a researcher, check with your institution. The easiest way to not worry about this is to properly cite your sources.
What If You Get Caught Plagiarizing?
Different institutions handle cases of plagiarism differently. Nonetheless, the consequence of plagiarism is serious and can result in some or all of the following:
- Academic probation
- Severe damage to reputation
- Legal action
- Expulsion from a course, or
- Failing a course
If you’re caught plagiarizing in a research publication, it will severely harm your reputation, not to mention your career as well.
You might even be banned from publishing ever again. So, make sure you avoid plagiarism altogether.
What makes plagiarism more serious is it can be grounds for legal action – especially if you are publishing research.
ᴀᴅᴠᴇʀᴛɪsᴇᴍᴇɴᴛ
Detect Plagiarism For Free With CopyChecker
Now that you know the common types of plagiarism, you will be able to avoid them better. You don’t have to manually check for plagiarism. Our free plagiarism checker makes the process much easier.







